Introduction
What is YAG Laser Welding?
YAG (yttrium aluminum garnet doped with neodymium) welding is a solid-state laser welding technique with a wavelength of 1.064 µm.
It excels in high-efficiency metal welding and is widely used in automotive, aerospace, and electronics industries.
Comparation to Fiber Laser Welding
|
Comparison Item |
Fiber Laser Welding Machine |
YAG Laser Welding Machine |
|
Structural Components |
Cabinet + Chiller |
Cabinet + Power Cabinet + Chiller |
|
Welding Type |
Deep Penetration Welding (Keyhole Welding) |
Heat Conduction Welding |
|
Optical Path Type |
Hard/Soft Optical Path (via fiber transmission) |
Hard/Soft Optical Path |
|
Laser Output Mode |
Continuous Laser Welding |
Pulsed Laser Welding |
|
Maintenance |
- No consumables - Nearly maintenance-free - Longer lifespan |
- Requires periodic lamp replacement (every ~4 months) - Frequent maintenance |
|
Beam Quality |
- Superior beam quality (close to fundamental mode) - High power density - High photoelectric conversion efficiency (multiple times that of YAG) |
- Poorer beam quality - Weaker focusing performance |
|
Applicable Material Thickness |
Suitable for thicker plates (>0.5mm) |
Suitable for thin plates (<0.5mm) |
|
Energy Feedback Function |
Not available |
Supports energy/current feedback (Compensates for voltage fluctuations, lamp aging, etc.) |
|
Working Principle |
- Uses rare-earth-doped fiber (e.g., ytterbium, erbium) as gain medium - Pump source excites particle transitions; laser transmits through fiber |
- YAG crystal as active medium - Pumped by xenon/krypton lamps to excite neodymium ions |
|
Device Characteristics |
- Simple structure (no complex optical cavities) - Low maintenance cost |
- Relies on xenon lamps (short lifespan) - Complex maintenance |
|
Welding Precision |
- Smaller weld spots (micron-level) - Ideal for high-precision applications (e.g., electronics) |
- Larger weld spots - Suitable for general metal structures (strength-focused scenarios) |

Different Between Fiber And YAG
Want To Know More About Laser Welding?
Start a Conversation Now!
FAQs
YAG, standing for yttrium-aluminum-garnet, is a type of laser that generates short-pulsed, high-energy beams for metal welding.
It is also referred to as a neodymium-YAG or ND-YAG laser.
The YAG laser also offers high peak powers in small laser sizes, which enables welding with large optical spot size.
YAG offers lower upfront costs and better suitability for thin materials, making it ideal for small workshops or budget-conscious projects.
Applicable Materials
Metals: Aluminum alloys (automotive frames), stainless steel (kitchenware), titanium (aerospace components).
Electronics: PCB boards, microelectronic connectors, sensor housings.
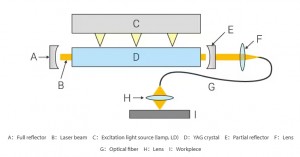
YAG Laser Welding System Diagram

YAG Laser Welding Machine
Typical Applications
Automotive: Battery tab welding, lightweight component joining.
Aerospace: Thin-walled structure repairs, turbine blade maintenance.
Electronics: Hermetic sealing of microdevices, precision circuit repairs.
Related Videos
Related Videos
Here are five intriguing facts about laser welding you might not know, from multi - function integration of cutting, cleaning, and welding in one machine with a simple switch, to saving on shielding gas costs.
Whether you're new to laser welding or a seasoned pro, this video offers unexpected handheld laser welding insights.
Recommend Machines
Post time: Apr-18-2025






