Handheld Laser Welding: A Complete Reference Guide

Table of Content:
Handheld Laser Welding:
Reference Sheet:
Intro:
Handheld laser welding offers numerous advantages, but it also requires meticulous attention to safety protocols.
This article will explore the key safety considerations for handheld laser welding.
As well as provide recommendations on shielding gas selection and filler wire choices for common metal types.
Handheld Laser Welding: Mandatory Safety
Personal Protection Equipment (PPE):
1. Laser Safety Glasses and Face Shield
Specialized laser safety glasses and a face shield are mandatory under laser safety guidelines to protect the operator's eyes and face from the intense laser beam.
2. Welding Gloves & Outfit
Welding gloves must be regularly inspected and replaced if they become wet, worn-out, or damaged to maintain adequate protection.
A fire-proof and heat-proof jacket, trousers, and working boots must be worn at all times.
These garments should be immediately replaced if they become wet, worn-out, or damaged.
3. Respirator with Active Air Filtration
A standalone respirator with active air filtration is required to protect the operator from harmful fumes and particles.
Proper maintenance and routine checks are essential to ensure the system is functioning correctly.
Maintaining a Safe Welding Environment:
1. Clearing the Area
The welding area must be clear of any flammable materials, heat-sensitive objects, or pressurized containers.
Including those near the welding piece, gun, system, and the operator.
2. Designated Enclosed Area
Welding should be conducted in a designated, enclosed area with effective light barriers.
To prevent the escape of the laser beam and mitigate potential harm or damage.
All personnel entering the welding area must wear the same level of protection as the operator.
3. Emergency Shut-Off
A kill switch linked to the entrance of the welding area should be installed.
To immediately shut off the laser welding system in case of unexpected entry.
Handheld Laser Welding: Alternative Safety
Personal Protection Equipment (PPE):
1. Welding Outfit
If specialized welding attire is unavailable, clothing that is not easily flammable and has long sleeves may be used as an alternative, along with appropriate footwear.
2. Respirator
A respirator that meets the required level of protection against harmful dust and metal particles can be used as an alternative.
Maintaining a Safe Welding Environment:
1. Enclosed Area with Warning Signs
If setting up laser barriers is impractical or unavailable, the welding area must be clearly marked with warning signs, and all entrances must be kept closed.
All personnel entering the welding area must have laser safety training and be aware of the invisible nature of the laser beam.
Prioritizing safety is paramount in handheld laser welding.
By adhering to the mandatory safety protocols and being prepared to adopt temporary alternative measures when necessary.
Operators can ensure a safe and responsible welding environment.
Laser Welding is the Future. And the Future Starts with You!
Reference Sheets
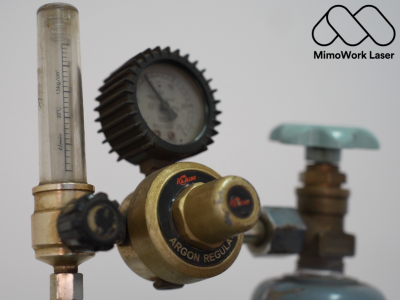
The information provided in this article is intended as a general overview of laser welding parameters and safety considerations.
Each specific welding project and laser welding system will have unique requirements and conditions.
It is strongly recommended to consult with your laser system provider for detailed guidelines.
Including recommendations, and best practices applicable to your particular welding application and equipment.
The general information presented here should not be solely relied upon.
As specialized expertise and guidance from the laser system manufacturer is essential for safe and effective laser welding operations.
Laser Welding Aluminum Alloy:
1. Material Thickness - Welding Power/ Speed
| Thickness (mm) | 1000W Laser Welding Speed | 1500W Laser Welding Speed | 2000W Laser Welding Speed | 3000W Laser Welding Speed |
| 0.5 | 45-55mm/s | 60-65mm/s | 70-80mm/s | 80-90mm/s |
| 1 | 35-45mm/s | 40-50mm/s | 60-70mm/s | 70-80mm/s |
| 1.5 | 20-30mm/s | 30-40mm/s | 40-50mm/s | 60-70mm/s |
| 2 | 20-30mm/s | 30-40mm/s | 40-50mm/s | |
| 3 | 30-40mm/s |
2. Recommended Shielding Gas
Pure argon (Ar) is the preferred shielding gas for laser welding of aluminum alloys.
Argon provides excellent arc stability and protects the molten weld pool from atmospheric contamination.
Which is crucial for maintaining the integrity and corrosion resistance of aluminum welds.
3. Recommended Filler Wires
Aluminum Alloy Filler Wires are used to match the composition of the base metal being welded.
ER4043 - A silicon-containing aluminum filler wire suitable for welding 6-series aluminum alloys.
ER5356 - A magnesium-containing aluminum filler wire suitable for welding 5-series aluminum alloys.
ER4047 - A silicon-rich aluminum filler wire used for welding 4-series aluminum alloys.
The wire diameter typically ranges from 0.8 mm (0.030 in) to 1.2 mm (0.045 in) for handheld laser welding of aluminum alloys.
It's important to note that aluminum alloys require a higher level of cleanliness and surface preparation compared to other metals.
Laser Welding Carbon Steel:
1. Material Thickness - Welding Power/ Speed
| Thickness (mm) | 1000W Laser Welding Speed | 1500W Laser Welding Speed | 2000W Laser Welding Speed | 3000W Laser Welding Speed |
| 0.5 | 70-80mm/s | 80-90mm/s | 90-100mm/s | 100-110mm/s |
| 1 | 50-60mm/s | 70-80mm/s | 80-90mm/s | 90-100mm/s |
| 1.5 | 30-40mm/s | 50-60mm/s | 60-70mm/s | 70-80mm/s |
| 2 | 20-30mm/s | 30-40mm/s | 40-50mm/s | 60-70mm/s |
| 3 | 20-30mm/s | 30-40mm/s | 50-60mm/s | |
| 4 | 15-20mm/s | 20-30mm/s | 40-50mm/s | |
| 5 | 30-40mm/s | |||
| 6 | 20-30mm/s |
2. Recommended Shielding Gas
A mixture of Argon (Ar) and Carbon Dioxide (CO2) is commonly used.
The typical gas composition is 75-90% Argon and 10-25% Carbon Dioxide.
This gas mixture helps stabilize the arc, provide good weld penetration, and protect the molten weld pool from atmospheric contamination.
3. Recommended Filler Wires
Mild Steel or Low-Alloy Steel filler wires are typically used for carbon steel welding.
ER70S-6 - A general purpose mild steel wire suitable for a wide range of carbon steel thicknesses.
ER80S-G - A higher strength low-alloy steel wire for better mechanical properties.
ER90S-B3 - A low-alloy steel wire with added boron for increased strength and toughness.
The wire diameter is usually chosen based on the thickness of the base metal.
Typically ranging from 0.8 mm (0.030 in) to 1.2 mm (0.045 in) for handheld laser welding of carbon steel.
Laser Welding Brass:
1. Material Thickness - Welding Power/ Speed
| Thickness (mm) | 1000W Laser Welding Speed | 1500W Laser Welding Speed | 2000W Laser Welding Speed | 3000W Laser Welding Speed |
| 0.5 | 55-65mm/s | 70-80mm/s | 80-90mm/s | 90-100mm/s |
| 1 | 40-55mm/s | 50-60mm/s | 60-70mm/s | 80-90mm/s |
| 1.5 | 20-30mm/s | 40-50mm/s | 50-60mm/s | 70-80mm/s |
| 2 | 20-30mm/s | 30-40mm/s | 60-70mm/s | |
| 3 | 20-30mm/s | 50-60mm/s | ||
| 4 | 30-40mm/s | |||
| 5 | 20-30mm/s |
2. Recommended Shielding Gas
Pure Argon (Ar) is the most suitable shielding gas for laser welding of brass.
Argon helps protect the molten weld pool from atmospheric contamination.
Which can lead to excessive oxidation and porosity in brass welds.
3. Recommended Filler Wires
Brass filler wires are typically used for welding brass.
ERCuZn-A or ERCuZn-C: These are copper-zinc alloy filler wires that match the composition of the base brass material.
ERCuAl-A2: A copper-aluminum alloy filler wire that can be used for welding brass as well as other copper-based alloys.
The wire diameter for brass laser welding is usually in the range of 0.8 mm (0.030 in) to 1.2 mm (0.045 in).
Laser Welding Stainless Steel:
1. Material Thickness - Welding Power/ Speed
| Thickness (mm) | 1000W Laser Welding Speed | 1500W Laser Welding Speed | 2000W Laser Welding Speed | 3000W Laser Welding Speed |
| 0.5 | 80-90mm/s | 90-100mm/s | 100-110mm/s | 110-120mm/s |
| 1 | 60-70mm/s | 80-90mm/s | 90-100mm/s | 100-110mm/s |
| 1.5 | 40-50mm/s | 60-70mm/s | 60-70mm/s | 90-100mm/s |
| 2 | 30-40mm/s | 40-50mm/s | 50-60mm/s | 80-90mm/s |
| 3 | 30-40mm/s | 40-50mm/s | 70-80mm/s | |
| 4 | 20-30mm/s | 30-40mm/s | 60-70mm/s | |
| 5 | 40-50mm/s | |||
| 6 | 30-40mm/s |
2. Recommended Shielding Gas
Pure Argon (Ar) is the most commonly used shielding gas for stainless steel laser welding.
Argon provides excellent arc stability and protects the weld pool from atmospheric contamination.
Which is crucial for maintaining the corrosion-resistant properties of stainless steel.
In some cases, Nitrogen (N) is also used for Laser Welding Stainless Steel
3. Recommended Filler Wires
Stainless Steel filler wires are used to maintain the corrosion resistance and metallurgical properties of the base metal.
ER308L - A low-carbon 18-8 stainless steel wire for general-purpose applications.
ER309L - A 23-12 stainless steel wire for welding dissimilar metals like carbon steel to stainless steel.
ER316L - A low-carbon 16-8-2 stainless steel wire with added molybdenum for improved corrosion resistance.
The wire diameter is typically in the range of 0.8 mm (0.030 in) to 1.2 mm (0.045 in) for handheld laser welding of stainless steel.
Laser Welding Vs TIG Welding: Which one is Better?
If you enjoyed this video, why not consider subscribing to our Youtube Channel?
Laser welding and TIG welding are two popular methods for joining metals, but laser welding offers distinct advantages.
With its precision and speed, laser welding allows for cleaner, more efficient welds with minimal heat distortion.
It’s easier to master, making it accessible for both beginners and experienced welders.
Additionally, laser welding can handle a variety of materials, including stainless steel and aluminum, with exceptional results.
Embracing laser welding not only enhances productivity but also ensures high-quality outcomes, making it a smart choice for modern fabrication needs.
Handheld Laser Welder [The 1 Minute Preview]
A single, handheld unit that can effortlessly transition between laser welding, laser cleaning, and laser cutting functionalities.
With a simple switch of the nozzle attachment, users can seamlessly adapt the machine to their specific needs.
Whether joining metal components, removing surface impurities, or precisely cutting materials.
This comprehensive laser toolset provides the ability to tackle a wide range of applications.
All from the convenience of a single, easy-to-use device.
If you enjoyed this video, why not consider subscribing to our Youtube Channel?
Machine Recommendations for Handheld Laser Welding
Here are some Laser-Knowledge you Might be Interested in:
Post time: Jul-12-2024







